Magnetic Penetrant Testing
Surface breaking or very near surface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials give rise to leakage fields when high levels of magnetic flux are applied. These leakage fields attract magnetic particles (finely divided magnetite) to themselves leading to the formation of an indication.
The magnetic particles may be visibly or fluorescently pigmented to provide contrast with the substrate or conversely the substrate may be lightly coated with a white background lacquer to contrast with the particles.
Fluorescent magnetic particles normally provide the greatest sensitivity in a liquid suspension, usually applied by spraying. In certain cases dry particles may be applied by a gentle jet of air. The technique is applicable only to ferromagnetic materials at a temperature below the Curie point (about 650°C).
The leakage field will be greatest for linear discontinuities at right angles to the magnetic field so for a comprehensive test the magnetic field must normally be applied in two directions, mutually perpendicular. The test is economical to carry out in terms of equipment cost and rapidity of inspection and the level of operator training required is relatively low.
Source :
Surface breaking or very near surface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials give rise to leakage fields when high levels of magnetic flux are applied. These leakage fields attract magnetic particles (finely divided magnetite) to themselves leading to the formation of an indication.
The magnetic particles may be visibly or fluorescently pigmented to provide contrast with the substrate or conversely the substrate may be lightly coated with a white background lacquer to contrast with the particles.
Fluorescent magnetic particles normally provide the greatest sensitivity in a liquid suspension, usually applied by spraying. In certain cases dry particles may be applied by a gentle jet of air. The technique is applicable only to ferromagnetic materials at a temperature below the Curie point (about 650°C).
The leakage field will be greatest for linear discontinuities at right angles to the magnetic field so for a comprehensive test the magnetic field must normally be applied in two directions, mutually perpendicular. The test is economical to carry out in terms of equipment cost and rapidity of inspection and the level of operator training required is relatively low.
Advantages
- Inexpensive equipment
- Direct location of defect
- Surface conditions not critical
- Can be applied without power
- Low skill level
- Sub-surface defects found 1-2mm
- Quick, instant results
- Hot testing (using dry powder)
- Can be used in the dark (UV light)
Limitations
- Only magnetic materials
- May need to demagnetise components
- Access may be a problem for the yoke
- Need power if using a yoke
- No permanent record
- Calibration of equipment
- Testing in two directions required
- Need good lighting - 500 lux minimum
Magnetic Penetrant testing
Magnetic Fluorescence Penetrant testing
CSWIP 3.1 - Welding Inspector WIS5, TWI Ltd, 2017.
_________________________________________________________________________________
Any liquid with good wetting properties will act as a penetrant, which is attracted into surface-breaking discontinuities by capillary forces. Penetrant which has entered a tight discontinuity will remain even when the excess is removed.
Radiographic Testing (RT) – This technique for weld testing makes utilization of X-beams, delivered by a X-beam tube, or gamma beams, created by a radioactive isotope. The fundamental rule of radiographic review of welds is the equivalent as that for medicinal radiography. Entering radiation is gone through a strong protest, for this situation a weld rather that piece of the human body, onto a photographic film, bringing about a picture of the question's inner structure being saved on the film. The measure of vitality consumed by the question relies upon its thickness and thickness. Vitality not consumed by the question will cause presentation of the radiographic film. These zones will be dim when the film is created. Territories of the film presented to less vitality stay lighter. In this manner, regions of the protest where the thickness has been changed by discontinuities, for example, porosity or splits, will show up as dull frameworks on the film. Considerations of low thickness, for example, slag, will show up as dull regions on the film while incorporations of high thickness, for example, tungsten, will show up as light territories. All discontinuities are identified by review shape and variety in thickness of the prepared film.
X-RAY RADIOGRAPHY:
_________________________________________________________________________________
Dye Penetration Testing
Any liquid with good wetting properties will act as a penetrant, which is attracted into surface-breaking discontinuities by capillary forces. Penetrant which has entered a tight discontinuity will remain even when the excess is removed.
Application of a suitable developer will encourage the penetrant within discontinuities to bleed out. If there is a suitable contrast between the penetrant and the developer an indication visible to the eye will be formed. Provided by either visible or fluorescent dyes.
Use of fluorescent dyes considerably increases the sensitivity of the technique. The technique is not applicable at extremes of temperature as at below 5°C the penetrant vehicle, normally oil, will become excessively viscous causing an increase in the penetration time with a consequent decrease in sensitivity.
Above 60°C the penetrant will dry out and the technique will not work.
Advantages
- All non porous materials
- Portable
- Applicable to small parts with complex geometry
- Simple
- Inexpensive
- Sensitive
- Relatively low skill level (easy to interpret)
Limitation
- Will only detect defects open to the surface
- Requires careful space preparation
- Not applicable to porous surfaces
- Temperature dependent
- Cannot retest indefinitely
- Potentially hazardous chemicals
- No permanent record
- Time lapse between application and results
- Messy
Normal Dye Penetrant Testing
Fluorescence Dye Penetrant Testing
Source :
CSWIP 3.1 - Welding Inspector WIS5, TWI Ltd, 2017.
________________________________________________________________________________
Radiographic Testing (RT) – This technique for weld testing makes utilization of X-beams, delivered by a X-beam tube, or gamma beams, created by a radioactive isotope. The fundamental rule of radiographic review of welds is the equivalent as that for medicinal radiography. Entering radiation is gone through a strong protest, for this situation a weld rather that piece of the human body, onto a photographic film, bringing about a picture of the question's inner structure being saved on the film. The measure of vitality consumed by the question relies upon its thickness and thickness. Vitality not consumed by the question will cause presentation of the radiographic film. These zones will be dim when the film is created. Territories of the film presented to less vitality stay lighter. In this manner, regions of the protest where the thickness has been changed by discontinuities, for example, porosity or splits, will show up as dull frameworks on the film. Considerations of low thickness, for example, slag, will show up as dull regions on the film while incorporations of high thickness, for example, tungsten, will show up as light territories. All discontinuities are identified by review shape and variety in thickness of the prepared film.
 |
| How NDT Radioactive works |
Radiographic testing can give a perpetual film record of weld quality that is moderately simple to translate via prepared staff. This testing strategy is generally suited to approaching the two sides of the welded joint (except for twofold divider flag picture methods utilized on some pipe work). Despite the fact that this is a moderate and costly strategy for nondestructive testing, it is a positive technique for recognizing porosity, incorporations, splits, and voids in the inside of welds. It is basic that qualified faculty direct radiographic translation since bogus elucidation of radiographs can be costly and meddle truly with profitability. There are clear wellbeing contemplations when leading radiographic testing. X-beam and gamma radiation is undetectable to the exposed eye and can have genuine heath and security suggestions. Just appropriately prepared and qualified work force should rehearse this sort of testing.
X-RAY RADIOGRAPHY:
Advantage:
- Detects surface and internal flaws
- Can inspect hidden areas
- Permanent test record obtained Minimum part preparation
Disadvantage:
- Safety hazard Very expensive (slow process)
- Highly directional, sensitive to flaw orientation
- High degree of skill and experience required for exposure and interpretation
- Depth of discontinuity not indicated
ISOTOPE RADIOGRAPHY:
Advantage:
- Portable Less expensive than Xray
- Detects surface and internal flaws
- Can inspect hidden areas
- Permanent test record obtained
- Minimum part preparation
Disadvantages:
- Safety hazard Must conform to Federal and State regulations for handling and use
- Highly directional, sensitive to flaw orientation
- High degree of skill and experience required for exposure and interpretation
- Depth of discontinuity not indicated
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) – This strategy for testing makes utilization of mechanical vibrations like sound waves yet of higher recurrence. A light emission vitality is guided into the protest be tried. This pillar goes through the protest with irrelevant misfortune, aside from when it is captured and reflected by an irregularity. The ultrasonic contact beat reflection method is utilized. This framework utilizes a transducer that progressions electrical vitality into mechanical vitality. The transducer is energized by a high-recurrence voltage, which makes a gem vibrate mechanically. The precious stone test turns into the wellspring of ultrasonic mechanical vibration. These vibrations are transmitted into the test piece through a coupling liquid, as a rule a film of oil, called a couplant. At the point when the beat of ultrasonic waves strikes an intermittence in the test piece, it is reflected back to its purpose of inception. Along these lines the vitality comes back to the transducer. The transducer presently fills in as a collector for the reflected vitality. The underlying sign or fundamental blast, the returned echoes from the discontinuities, and the reverberate of the back surface of the test piece are altogether shown by a follow on the screen of a cathode-beam oscilloscope. The identification, area, and assessment of discontinuities wind up conceivable on the grounds that the speed of sound through a given material is almost steady, making separation estimation conceivable, and the general sufficiency of a reflected heartbeat is pretty much relative to the span of the reflector.
A standout amongst the most valuable qualities of ultrasonic testing is its capacity to decide the correct position of an irregularity in a weld. This testing technique requires an abnormal state of administrator preparing and fitness and is dependant on the foundation and use of reasonable testing methods. This testing technique can be utilized on ferrous and nonferrous materials, is regularly suited for testing thicker segments available from one side just, and can frequently identify better lines or plainer imperfections which may not be as promptly recognized by radiographic testing.
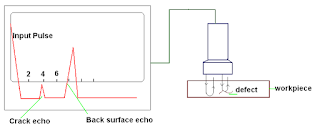 |
| NDT UltraSonic Testing |
 |
| NDT Ultra sonic how it works |
Advantages of ultrasonic inspection as a method of Non-Destructive Examination are:
- Internal defects can be detected and sized when a validated procedure is applied
- Thick specimens take no more time to examine than thin ones, assuming correct instrumentation setup
- Access to only one side of the component is needed
- There is no radiation hazard in ultrasonic examination, and hence no disruption of work as there iswith radiography
- Volumetric and crack like defects can be detected, irrespective of their orientation
Disadvantages of ultrasonic inspection as a method of Non-Destructive Examination are:
- A high degree of operator skill and integrity is needed. Hence, the need for trained and certified NDT personnel
- In most examinations, there is no permanent record of the inspection as there is in radiography, however more recent equipment does offer this facility
- In certain materials, like austenitic steel, the large grain size found in welds can cause attenuation and this may mask defects
- Spurious indications, and the misreading of signals, can result in unnecessary repairs, which is why a validated procedure should be applied when carrying out any ultrasonic examination.

Comments
Post a Comment